
Blazor and Razor have a healthy following in the web UI dev community, especially among developers who primarily work within .NET Core. However, the confusion between these two can be off-putting for some developers, especially beginners.
This post discusses the similarities and differences between Blazor framework and Razor; both are part of Microsoft’s free and open source .NET Core development platform. We also discuss where these two technologies merge and how you will likely use them in your projects.
What Is C# Blazor and Razor?
Introduced in 2018, Blazor is a modern web development framework from Microsoft used to develop server-side and client-side web interfaces using C# as the primary language. You can use Blazor to develop fast interfaces that run on the server or entirely on the client’s browser with Web Assembly (WASM) open standards. Blazor can also be used to build progressive offline applications.
Blazor is seen as the next step in Microsoft’s web development plan because it combines the versatility and reliability of ASP .NET Core with modern web technologies such as Web Assembly. Many modern applications built within .NET Core will likely use Blazor. We’ll detail Blazor’s structure and how you can use it in your projects later.
On the other hand, Razor is the default page-based Web UI technology in ASP .NET Core. On its own, Razor is more of a templating engine you can use mainly to build fast, lightweight, and dynamic web pages. Razor has its own syntax, which is basically C# combined with HTML markup and CSS.
Note to beginner devs: There is some confusion regarding these two technologies mainly because Razor pages and syntax are also used within the Blazor framework to build server-side or client-side UI elements. The word “Blazor” is a combination of the terms browser and Razor, which alludes to the fact that Blazor can execute Razor views or web UI on the browser.
Razor Pages in ASP.NET Core Explained - How to Use It
Razor is one of the more established server-side web UI technologies within the ASP .NET Core web development framework. It is the best solution for building simple or lightweight server-rendered web UI’s with C# where the focus is on the page’s appearance and individual elements. For instance, you can use Razor to build a single-page user registration interface with CRUD functionality.
One interesting and often confusing thing about Razor is that it is used present in other web frameworks within ASP.NET Core. You will encounter Razor it ASP.NET Core MVC, Blazor, Xamarin, Mono, and other places. However, Microsoft made it possible to construct pages and views with Razor independent of the other frameworks.
Tip: To avoid confusion, it’s advisable to choose just one web UI technology within ASP.NET Core and run with it to the end. For instance, do not start using Blazor and later switch to the MVC framework on the same project unless you have a very good reason. Start with Razor for learning purposes, then move on to other project types.
When to Use Razor Pages
You Are Building server-side web UI — As an independent templating engine, Razor is primarily used to build web UI’s that are rendered from the server side. You can also use it inside an MVC application on the webserver to produce HTML and CSS dynamically.
You are Building frequently updated web UI — Server-side web UI’s built using Razor are meant to be dynamic or frequently updated, much like what you could do with a content management system (CMS). Creating your dynamic web Ui with Razor allows you to control the design, features, behavior, updates, configuration options, speed, etc.
You are building Cross-platform Web UIs — Being part of ASP.NET Core, any interfaces or pages you create with Razor can be used on the web and across all computing platforms (Windows, Linux, Mac, and mobile). Razor is the preferred templating engine for progressive ASP .NET Core apps and hybrid applications that use an embedded WebView.
You are learning ASP.NET Core — According to Microsoft, building plain razor pages is the easiest way to start building web UIs within .NET Core because of the syntax and simplified application structure. Of course, you will also find it easier to start working on complex projects in Blazor or ASP. NET core MVC.
You have experience with Web Forms — Razor is the replacement web UI technology within ASP .NET, the now discontinued web forms previously used in the ASP .NET framework. You’ll be able to do almost everything you could and more with web forms using Razor markup.
You prioritize speed and performance — Razor produces lightweight, performance-oriented server-side pages that load fast on any device. The fact that the UI elements are loaded from the web server also means that you can target any device with low processing power and memory.
You are working with secure resources — Razor separates application logic from the UI, allowing you to create secure applications. You’ll use Razor markup to create your UI, but the application logic will be implemented using C# or another backend technology. Communication between the client and the server will be done using a real-time messaging framework like SignalR or through an API.
To create simple static pages within ASP.NET — If all you want to do is create a normal non-interactive website with a series of related pages and forms, Razor is the best option for you. You can build your entire website with Razor markup on the server side and deploy it on a normal hosting service.
When Not to Use Razor Pages
You will see Razor in all the web development frameworks or project types within ASP. Net Core. With this in mind, there aren’t any specific instances where you will need to avoid using it on projects. However, it’s important to note that Razor, as an independent technology, cannot be used to create client-side web UI without Blazor.
Blazor in .NET Core Explained - How And When To Use It
Blazor is a new web UI framework inside ASP.NET Core used to build fast server-side and client-side applications. Blazor has two deployment models:
Blazor Server-Side
You can use .NET Core Blazor to create server-side web UI. In this app model, your entire app is hosted and executed on a remote web server, and the user-browser only receives rendered UI elements in HTML and CSS format. Communication between the client and the server is handled through SignalR to enable real-time web functionality. The SignalR library is part of ASP.NET Core and is free and open source.
Examples of Applications You can create with Blazor server-side include social networks, GPS apps, live blogs, gaming apps, and e-commerce applications. All these apps require a constant connection to the web server for real-time updates. SignalR enables fast data uploads and downloads between the client and the server to make app UI updates faster and more fluid.
Blazor Client-Side
Blazor can also be used to create client-side web UI using web assembly. A web application developed using Blazor web assembly executes on the user’s browser, and HTML and CSS are generated automatically. Blazor WebAssembly applications are meant to be interactive to support user actions such as clicking and moving items. For example, you could develop a photo editing web application UI using Blazor WebAssembly. However, Blazor Wasm is not recommended for security-sensitive apps.
Components in Blazor
A .NET Core Blazor web UI project is divided into C# classes or components, allowing the app to be split into independent elements consisting of C# code and HTML markup. Components in .NET Core Razor are Razor pages customized to match the framework’s rules. This means developers familiar with Razor or the MVC can easily develop within Blazor.
Build Hybrid applications with Blazor
One advantage Blazor has over Razor is that you can use it to create hybrid or progressive web applications that can be installed on desktops and mobile devices. Hybrid applications developed using Blazor use an embedded browser and can run offline.
Razor Pages and Blazor Examples
Here is a simple beginner-friendly tutorial demonstrating how to build a simple web UI.
What You’ll Need
Visual Studio 2022 — As a beginner in .NET core web development, it’s better to use Visual Studio Community as your IDE. Visual Studio comes with the .NET Core software development kit (SDK) and runtime.
Important: Once downloaded and installed, ensure you install the ASP. NET and web development workload inside Visual Studio 2022.
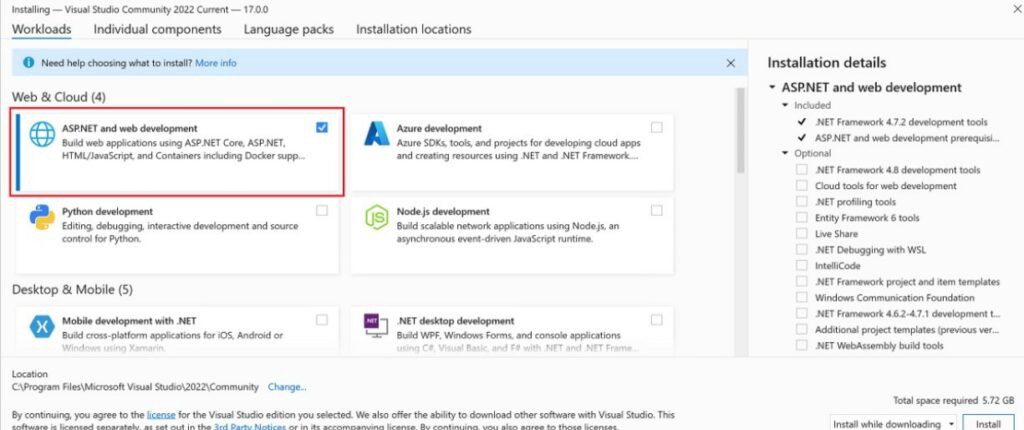
You can also opt to use a text editor like VS Code and install the .NET Core 6.0 SDK and C# for Visual Studio code extension separately. However, this option can be confusing for beginners unfamiliar with .NET Core.
A web browser — Your development computer should have a web browser to test your Razor application.
In addition to these tools, you’ll need a basic understanding of C#, developing with .NET core, and working knowledge of HTML and CSS.
Creating your First Razor Application
Step 1: Launch Visual Studio 2022. On the “Get Started” column, click on the last tab that says “Create a new project.”
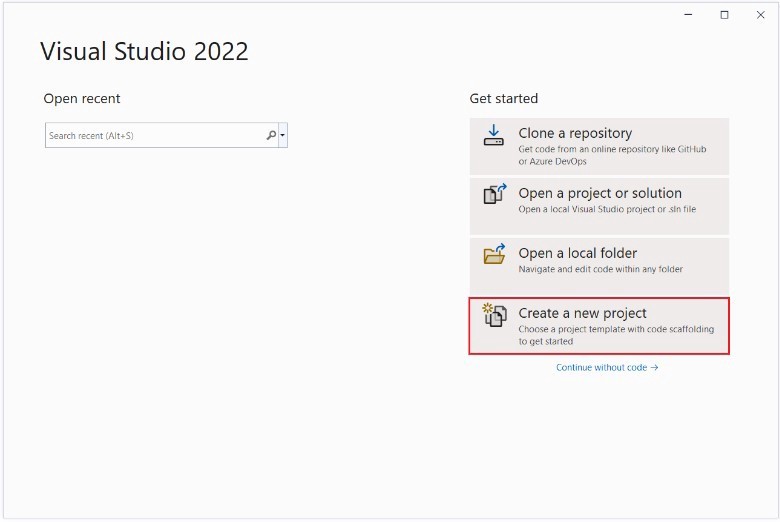
Step 2: In the open dialog, click on the option “ASP.NET Core Web App” and click Next.
Step 3: The next dialog box allows you to configure your Razor web application. In the “project name” text box, enter “MyFirstRazor.” You can change the location where your project will be stored or leave it as default, then click next to go to the next step.
Step 4: The next dialog box allows you to choose your target framework and other details. Under “framework”, choose .NET 6.0(Long term support). Check the box that says “Configure for HTTPS” and click create to create your first Razor pages app.
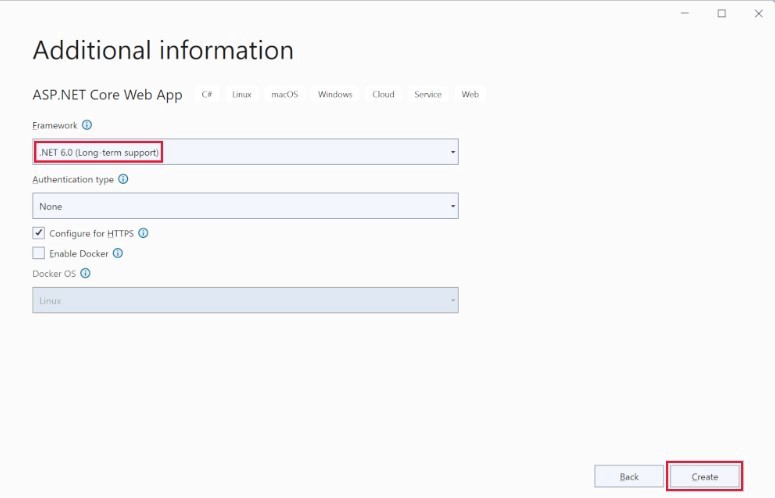
Step 5: Your Razor app project will be created, and you’ll be able to view its various components on the solutions explorer pane on the left of your IDEs interface. Most of the files are autogenerated by the IDE and are not meant to be edited or moved.
Last Step: Test Run — To check that your app was properly configured and ready for the web, locate it on the solutions explorer pane, click on it, then click run.
Click yes on the information box informing you about the SSL certificate to allow the ASP.NET auto-generated SSL certificate to be used while testing in a live browser.
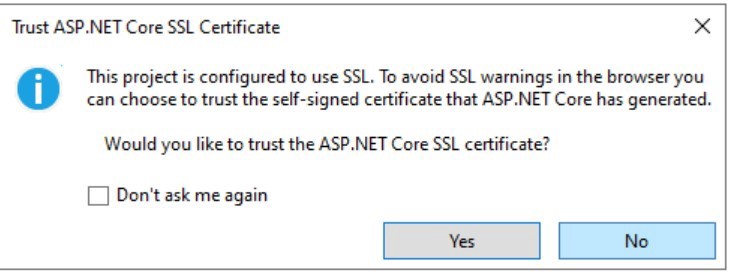
Click yes in the next security warning box to continue to the next step. The new app will be launched on your default browser, but it will display a black page for now.
Next Steps: Take time to learn how the Razor project folder is structured and how you can customize your application using C# and HTML markup.
Create Your First App with Blazor
Step 1: Launch Visual Studio and create a new project, then choose “new Blazor app” in the next dialog box.
Step 2: Configure your project, give it a name, then click next.
Step 3: Choose “Blazor WebAssembly App” in the next dialog box and click create.
Step 4: Locate the new component in the project folder and enter the following code.
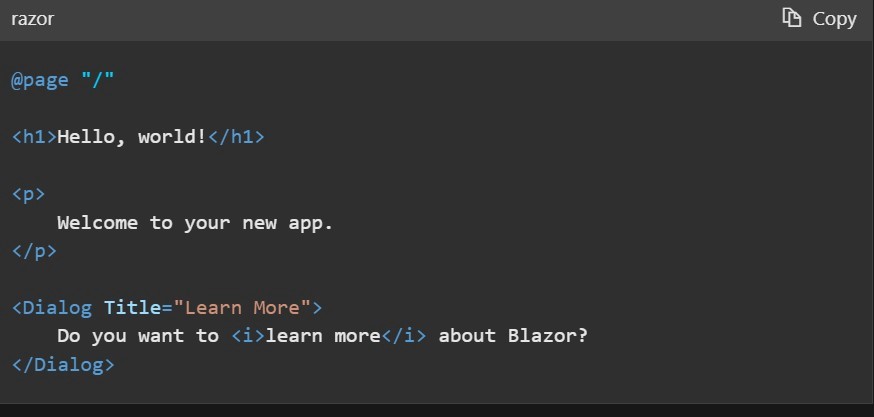
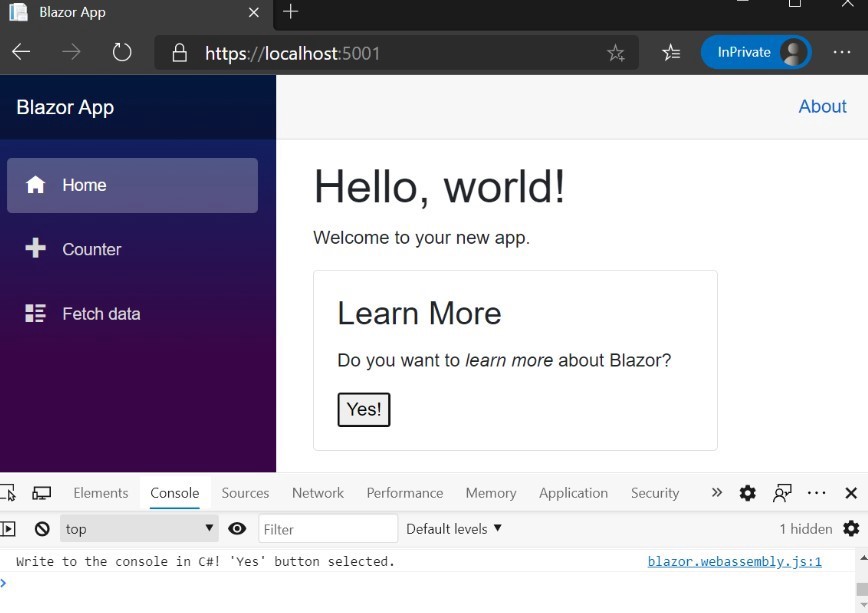
Run the project by pressing F5 and your keyboard, and you will see the following output on your default browser.
Can We Use C# Both for Server-Side and Client-Side Development?
C# is used across all project types within .NET Core. You can use it to create server-side applications inside .NET Core Standard, .NET Razor Pages, .NET Core MVC, and .NET Core Blazor. It’s the default programming language in .NET Core and can be used to create any application. C# Is free and open source.
All in all, both Blazor and Razor are solid web UI development technologies under the .NET Core family. The two can be used to create modern web UIs for web applications that are fast, secure, and reliable. New developers tend to lean towards Blazor because it has a better deployment model and is easier to learn than Razor. Hire a developer today to build fast, future-proof web applications with Blazor and Razor.