In recent years, large language models have emerged as groundbreaking advancements in natural language processing, revolutionizing how machines understand and generate human-like text. With their ability to process and comprehend vast amounts of unstructured data, these models have opened new possibilities for applications across various industries.
This article delves into the fascinating world of large language models, exploring their underlying technology, use cases, challenges, and their promising future. Continue reading to unravel the intricacies of these powerful language models and their transformative impact on communication, automation, and innovation.
What are Large Language Models?
Large language models (LLMs) are transformer-based models that undergo extensive training on vast amounts of text data. They are designed to generate natural-sounding and contextually relevant text across various styles and formats. A transformer model works on an attention mechanism to process long sequences of input text using encoder-decoder blocks. The encoder block generates numerical representations of input text known as embeddings and the decoder block analyzes these embeddings to generate relevant output sequences of text, as shown below.
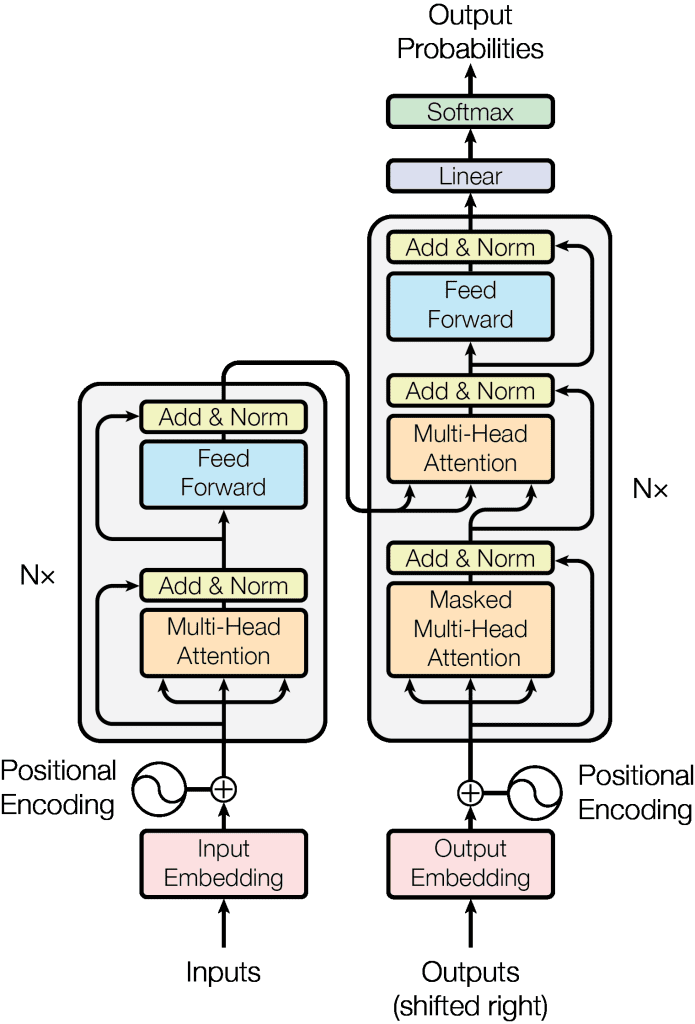
An illustration of a basic encoder-decoder transformer architecture that is used to build large language models.
Large language models are characterized by their significant size, typically spanning tens of gigabytes, and the immense number of parameters they possess, often reaching into the trillions. Parameters represent the values a model can independently update as it learns from training data. These learned values contribute to the model’s proficiency in solving specific language-processing tasks, such as text generation.
By leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms, large language models can interpret, translate, and summarize complex natural language texts. They are trained on massive datasets to acquire an understanding of grammar, syntax, and world knowledge, allowing them to generate human-like sentences that are often indistinguishable from those written by humans.
Evolution of Large Language Models
The pursuit of enabling machines to process and communicate in natural language has been a longstanding goal in artificial intelligence since the 1950s. Initially, supervised learning approaches were prevalent, but as data became more complex, unsupervised learning methods emerged to train models on vast amounts of unstructured data. This paved the way for the development of the Transformer model in 2017, which marked a significant milestone in large language models. The transformer model is a deep learning architecture that utilizes self-attention mechanisms to process and understand the contextual relationships between words in a sequence.
Building upon the transformer architecture, subsequent models like Google’s BERT and other transformer variants pushed the boundaries of large language models, incorporating millions of parameters and exhibiting greater sophistication. In 2020, OpenAI introduced GPT-3, a groundbreaking model with over a hundred billion parameters. GPT-3 showcased remarkable language generation capabilities and became a prominent example of the potential of large language models.
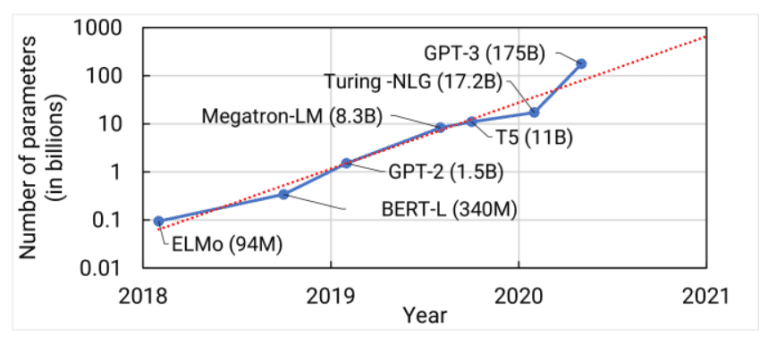
History and Evolution of LLMs
Continuing the evolution, OpenAI released ChatGPT, a prototype of GPT-4, in November 2022. Owing to the rapid self-improving capabilities of large language models, OpenAI released GPT-4 in March 2023. GPT-4 demonstrated advancements in problem-solving abilities, leveraging its vast general knowledge to tackle challenging tasks with increased accuracy.
The continuous refinement and development of large language models have led to significant strides in natural language processing and opened up new avenues for applications across various domains.
How do Large Language Models work?
Large language models operate through a series of crucial processes that enable them to understand and generate human-like text.
At the core of their architecture is the transformer model. Transformers enable the parallel processing of words in a text sequence, called tokens, using self-attention mechanisms. This mechanism allows the model to assign varying degrees of importance to different tokens, considering their relationships within the input sequence. As a result, transformers efficiently capture long-range dependencies within the text, making them highly effective for processing large-scale language tasks.
Training a large language model is a two-step process, including pre-training and fine-tuning. In pre-training, the models learn from vast amounts of unlabeled text data, predicting the next word in a sentence and capturing the language’s statistical patterns and linguistic structures. Fine-tuning then specializes the models for specific tasks or datasets with labeled examples, refining their abilities to generate contextually relevant text.
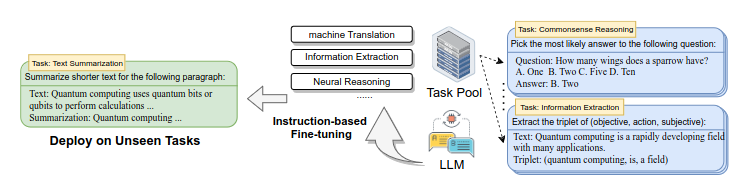
Overview of fine-tuning an LLM with explicit instructions across various domains
During training, the models learn to predict the next word or token based on the context of preceding words. This process helps the models grasp the statistical patterns, grammar, syntax, and world knowledge embedded in the language. Additionally, contextual word embeddings enhance the models’ understanding by representing each word or token as an embedding that captures its meaning in the given context. These embeddings update dynamically as the model processes the input, enabling the models to generate coherent and context-sensitive text.
Why are Large Language Models important?
Large language models have emerged as a crucial technology with profound importance across various domains. Their advanced natural language processing capabilities make them invaluable tools in almost any industry. They have become indispensable assets for automating language-related tasks, freeing human resources, and enhancing organizational efficiency.
Large language models can generate creative and contextually relevant content, assist decision-making processes, and enhance search engines, chatbots, virtual assistants, and recommendation systems. Moreover, they foster innovation by providing powerful language processing capabilities previously unavailable at such scale and accuracy. They have opened the world to new possibilities for content creation, customer service automation, information retrieval, and personalized user experiences. Their versatility and adaptability allow them to be applied across diverse industries such as healthcare, finance, marketing, education, and entertainment.
The importance of large language models lies in their ability to revolutionize how we interact with and utilize language. They have the potential to streamline operations, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Classification of Large Language Model use cases
Large language models have garnered significant attention and importance due to their transformative capabilities in natural language processing. Their impact spans across industries, offering solutions for a diverse variety of tasks. Here are some specific use cases where large language models have demonstrated their effectiveness.
- Text Generation: Large language models can automate text-based content generation for a variety of purposes. Examples of use cases for text generation include content such as articles, blogs, research papers, social media posts, product descriptions, source codes, emails, and more.
- Language Translation: Large language models can translate text from one language to another with impressive accuracy and fluency. Language service providers, global companies, and even individuals can leverage them for real-time translation, localization, and breaking down language barriers in communication.
- Classification: Large language models also possess remarkable organization capabilities covering text classification, analysis, and categorization based on predefined labels or topics. These models can automate the management of vast amounts of textual data, making them valuable for tasks like sentiment analysis, spam detection, content moderation, and customer feedback analysis.
- Summarization: Large language models can summarize lengthy texts or documents into concise and coherent summaries. This is particularly useful for writing news articles, research papers, legal documents, and other content where extracting key information is essential.
- Virtual Assistance: Large language models are vital in powering virtual assistants and chatbots. They can understand user queries, provide relevant information, and engage in natural language conversations. These virtual assistants can assist with customer support, provide personalized recommendations, answer questions, and automate routine tasks, improving user experiences and increasing operational efficiency.
5 major applications of Large Language Models across industries
The applications of large language models are diverse and extensive, with their utilities across various domains. Here are a few industries that have employed large language models to improve their products and services:
1. Healthcare
Large language models have shown great promise in healthcare by powering clinical decision support systems. They can:
- Analyze patient data, medical records, and scientific literature to assist healthcare professionals in making accurate diagnoses and treatment decisions.
- Facilitate medical literature research, allowing researchers to efficiently access and extract relevant information from vast repositories of scientific articles.
- Aid in predicting drug-target interactions and generate potential new drug compounds that can contribute to drug discovery.
2. Finance
Large language models are vital to the finance sector, aiding them in risk assessment while catering to their sensitive data security and privacy requirements. Specifically, these models can:
- Analyze large volumes of financial data, market trends, and news articles to provide insights on investment risks, fraud detection, and market volatility.
- Contribute to algorithmic trading by processing real-time market data and generating predictions.
3. Ecommerce
Large language models are crucial in e-commerce applications, particularly product recommendation systems. They can:
- Generate personalized recommendations by analyzing customer data, browsing history, and product descriptions for improved user experiences and sales.
- Generate content for e-commerce platforms, automatically generating product descriptions, marketing copy, and social media posts.
4. Marketing
The marketing sector works with a sea of data, hiding gems of valuable customer and product insights. These insights can only be extracted using advanced technologies like large language models. These models can:
- Analyze and understand customer sentiment through sentiment analysis of a customer’s online activities and interactions.
- Traverse product data to forecast future trends.
- Extract valuable insights into consumer preferences by navigating social media posts, customer reviews, and online discussions
- Help marketers tailor their strategies, target specific audiences, and develop effective advertising campaigns.
5. Customer service
Large language models have revolutionized customer service by deploying chatbots and automated email responses. These LLM-powered chatbots can do it all:
- Interact with customers in natural language
- Address customer queries
- Provide information
- Offering assistance
Automating these services improves response times, enhances customer experiences, and reduces the burden on human support teams.
What are the challenges associated with Large Language Model development?
While large language models hold immense potential in revolutionizing natural language processing, their development comes with a set of unique challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. Following are some of the key hurdles associated with large language model development.

Cost-Intensive architecture
Operationalizing large language models can be resource-intensive. Distributing billions of parameters across multiple processing engines and memory blocks requires extensive specialized hardware with substantial investments. The costly infrastructure requirements of training and deployment of large language models can hinder access to smaller organizations with limited resources.
Language misuse (Biases and Falsities)
Large language models learn from vast amounts of data from all over the internet. Collecting large-scale heterogeneous data risks propagating biases stemming from disparate data sources. This can lead to biased or misleading outputs generated by the models. Addressing biases and ensuring that large language models produce fair and unbiased results is an ongoing challenge in the development process.
Requirement of large-scale training data
Adequate training of large language models requires massive amounts of high-quality training data. Access to such extensive and diverse datasets can be challenging, particularly for specialized domains or languages with limited resources. Obtaining and curating large-scale training data can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Explainability issues
Large language models are often characterized by their black-box nature, making understanding the reasoning behind their predictions or generated outputs challenging. The lack of explainability can be a barrier in domains where interpretability and transparency are crucial, such as legal or healthcare applications.
Dependence on high technical expertise
Developing and fine-tuning large language models requires highly technical expertise in machine learning, natural language processing, and computational linguistics. It can be challenging for organizations lacking in-house expertise to navigate the complexities of model development and implementation.
How to address the challenges of Large Language Models using knowledge graphs?

While the challenges of developing large language models seem daunting, they can be handled or even mitigated by augmenting the capabilities of these models. This is where knowledge graphs come in.
Knowledge graphs are structured, graphical representations of knowledge that capture relationships and facts. The integration of knowledge graphs with large language models holds great potential for advancing the development of more accurate, reliable, and responsible language models. Here are the different ways knowledge graphs and large language models can complement each other:
- Addressing biases: Integrating a knowledge graph with a large language model involves aggregating different data types and loading them into the model to create a comprehensive knowledge base. Knowledge graphs can act as a reliable source of factual information, helping large language models make more accurate and unbiased predictions and responses.
- Enhanced explainability: These graphs can also enhance the explainability of large language models by providing structured context for the generated text, making it easier to trace how the model arrived at a particular prediction.
- Domain specialization: By integrating external knowledge from the graph, large language models can enhance their understanding of specific domains and improve performance in specialized tasks, for example, drug discovery in healthcare. Knowledge graphs can provide additional context, facts, and relationships that are not explicitly present in the original training data, enriching the model’s knowledge base.
- Personalization: Knowledge graphs provide a rich, semantic framework of structured information that large language models can leverage to tailor responses based on the specific context of the input, enabling them to generate more contextually relevant and personalized responses.
What does the future hold for Large Language Models?
The future of large language models holds exciting possibilities. Advancements in research and development are expected to lead to models with a highly sophisticated understanding of language, enabling more nuanced and context-aware interactions. Large language models will likely evolve into domain-specific models, catering to specialized fields such as healthcare, law, finance, and more. Additionally, they are anticipated to enhance their multi-modal capabilities, seamlessly processing and generating text, audio, image, and video data. With a growing emphasis on ethical AI, the future of large language models will prioritize responsible development, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in their design and deployment.