Writing unit test code when using the Dapper ORM tool for database operations with ASP.NET Core Web Application

How to write unit tests with Dapper
Writing unit tests when using the Dapper ORM tool for database operations in an ASP.NET Core Web Application can be complex. This is because Dapper uses static extension methods that are difficult to mock when testing services.
There is one approach to resolving this problem. We need to create a generic database service which uses Dapper implementation with the interface of that service. We can inject the database service using dependency injection. Then we can mock that database service when using it for other services.
Let’s try this approach with a code example.
Prerequisites
Before trying this approach, you should have some basic knowledge about unit testing with ASP.NET Core Web application and you need to have the following tools installed:
Note: Here I am not creating the ASP.NET Web Application project.
Create a database service using the Dapper implementation
First, create the generic service for database service using the dapper implementation. You have to create an interface called IDbService for that.
public interface IDbService
{
Task<T> GetAsync<T>(string command, object parms);
Task<List<T>> GetAll<T>(string command, object parms );
Task<T> Insert<T>(string command, object parms);
Task<T> Update<T>(string command, object parms);
}
Now you have to create the implementation of the IDbService interface. In that case, You need to create a class called DbService which inherits the IDbService interface to implement it.
public class DbService : IDbService
{
private readonly IDbConnection _db;
private readonly IConfiguration _configuration;
public DbService(IConfiguration config)
{
_configuration = config;
_db = new NpgsqlConnection(_configuration.GetConnectionString("Employeedb"));
}
public async Task<T> GetAsync<T>(string command, object parms)
{
return (await _db.QueryAsync<T>(command, parms).ConfigureAwait(false)).FirstOrDefault();
}
public async Task<List<T>> GetAll<T>(string command, object parms)
{
return (await _db.QueryAsync<T>(command, parms)).ToList();
}
public async Task<T> Insert<T>(string command, object parms)
{
T result;
result = _db.Query<T>(command, parms, transaction: null, commandTimeout:60,commandType :CommandType.Text).FirstOrDefault();
return result;
}
public async Task<T> Update<T>(string command, object parms)
{
T result;
result = _db.Query<T>(command, parms, transaction: null, commandTimeout:60,commandType :CommandType.Text).FirstOrDefault();
return result;
}
}
We have used IConfiguration which using to access the appsettings.json file to get the connection string. Then we can use a connection string to connect with the PostgreSQL server.
Here, we have implemented the generic database service which can reuse inside any service as needed. Now you can avoid writing the database operations with dapper inside the services.
Create Employee Service
Now you have to create the employee service to get the employee details for this example application. Then we can use that method to write unit testing code.
You need to create an interface called IEmployeeService like the below code.
public interface IEmployeeService
{
Task<Employee> GetEmployee(int id);
}
Now you need to create the implementation of the IEmployeeService interface. In that case, you need to create a class called EmployeeService which inherits the IEmployeeService interface to implement it.
public class EmployeeService : IEmployeeService
{
private readonly IDbService _dbService;
public EmployeeService(IDbService dbService)
{
_dbService = dbService;
}
public async Task<Employee> GetEmployee(int id)
{
var employee = await _dbService.GetAsync<Employee>("SELECT * From public.employee where id=@id", new {id});
if (employee == null)
throw new Exception("There isn't employee with provided details");
return employee;
}
}
Here, you can see that we have injected the IDbService interface using the dependency injection for this service. Also, we have implemented the GetEmployee method which is used to get employee details using the database service.
Note: you need to register these services using the program.cs like the below code example.
builder.Services.AddScoped<IDbService, DbService>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<IEmployeeService, EmployeeService>();
Write a unit test using moq and xUnit
Here, we will use xUnit to write the unit test code for this code example application. Also, we’ll use moq package to mock the database service to write a unit test. In that case, create the new xUnit unit testing project for your solution like the below figure.
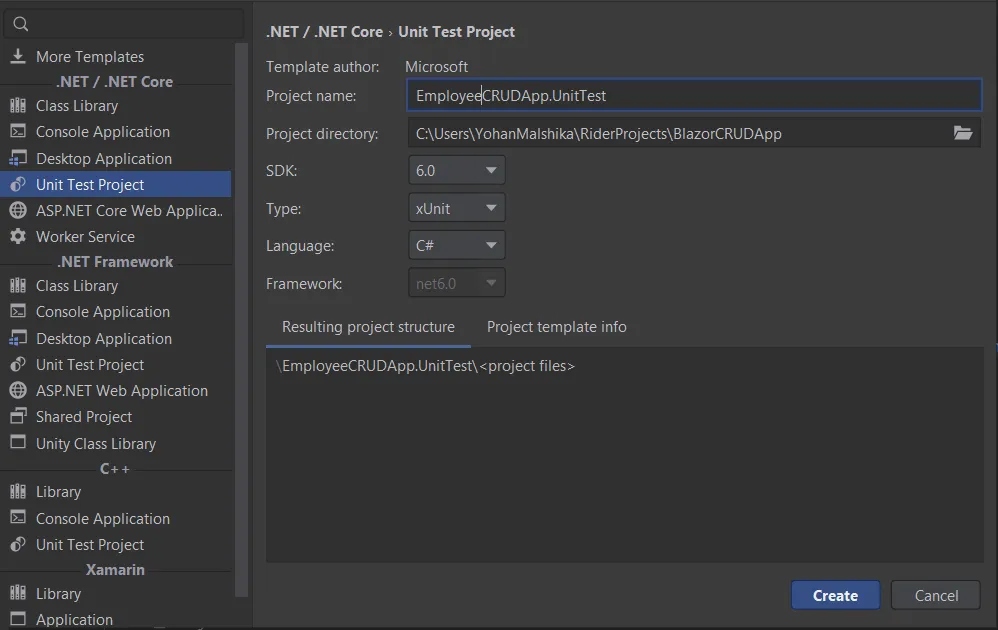
Create unit test project for ASP.NET Core Web Application
Then create the class called EmployeeServiceUnitTest to write the unit tests for EmployeeService class which we create above.
public class EmployeeServiceUnitTest
{
private readonly Mock<IDbService> _dbService = new();
[Fact]
public async void GetEmployee()
{
var employee = GetEmployeeDetails();
_dbService.Setup(s => s.GetAsync<Employee>(It.IsAny<string>(), It.IsAny<object>())).ReturnsAsync(employee);
var employeeService = new EmployeeService(_dbService.Object);
var result = await employeeService.GetEmployee(1);
Assert.Same(employee, result);
}
private Employee GetEmployeeDetails()
{
var employee = new Employee()
{
Id = 1,
Name = "Danula Nimneth",
Age = 18,
Address = "Kalutara, Sri Lanka",
MobileNumber = "0701234567"
};
return employee;
}
}
Here, we have mocked the IDbService which uses the database operations with dapper implementations. Here, we have mocked the GetAsync<T> method of the IDbService. In that case, we don’t need to connect with the database to test the unit test code.
Unit test case
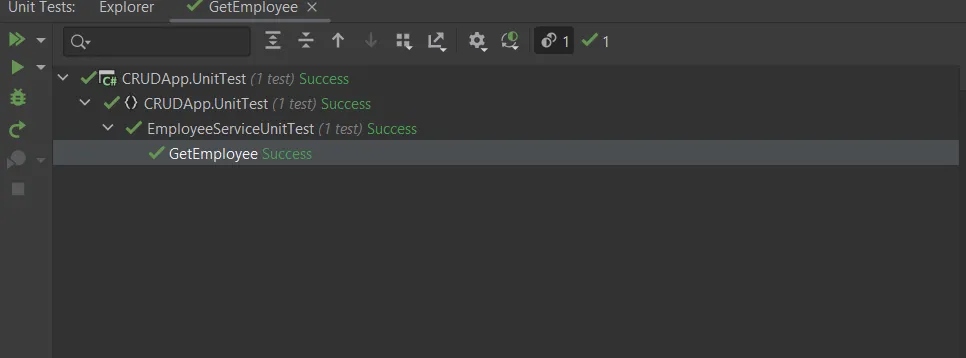
Here, you can see that our unit test code successfully passed.
Now you don’t need to write the dapper database operations inside the other services. Then it makes it difficult to mock the functions.
• • •
Conclusion
We can use database service as a generic service when using dapper database operations. It will help to reuse it inside the other services. And help to maintain code as clean code. Also, It will help to write unit testing easily.