
Today, we are going to cover uploading and downloading multiple files using ASP.Net Core 5.0 Web API by a simple process.
Note: This same technique works in .Net Core 3.1 and .Net Core 2.1 as well.
Begin with creating an empty web API project in visual studio and for target, framework choose .Net 5.0.
No external packages were used in this project.
Create a Services folder and inside that create one FileService class and IFileService Interface in it.
We have used three methods in this FileService.cs
- UploadFile
- DownloadFile
- SizeConverter
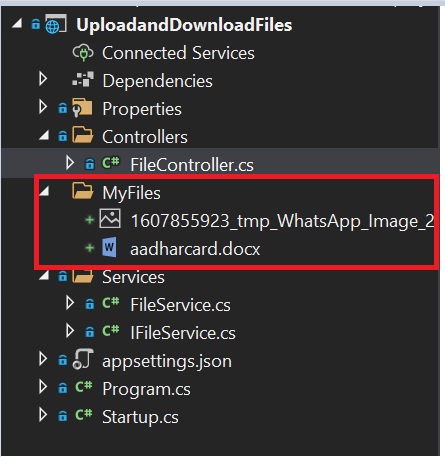
Since we need a folder to store these uploading files, here we have added one more parameter to pass the folder name as a string where it will store all these files.
FileService.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.IO.Compression;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace UploadandDownloadFiles.Services
{
public class FileService : IFileService
{
#region Property
private IHostingEnvironment _hostingEnvironment;
#endregion
#region Constructor
public FileService(IHostingEnvironment hostingEnvironment)
{
_hostingEnvironment = hostingEnvironment;
}
#endregion
#region Upload File
public void UploadFile(List<IFormFile> files, string subDirectory)
{
subDirectory = subDirectory ?? string.Empty;
var target = Path.Combine(_hostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath, subDirectory);
Directory.CreateDirectory(target);
files.ForEach(async file =>
{
if (file.Length <= 0) return;
var filePath = Path.Combine(target, file.FileName);
using (var stream = new FileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create))
{
await file.CopyToAsync(stream);
}
});
}
#endregion
#region Download File
public (string fileType, byte[] archiveData, string archiveName) DownloadFiles(string subDirectory)
{
var zipName = $"archive-{DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy_MM_dd-HH_mm_ss")}.zip";
var files = Directory.GetFiles(Path.Combine(_hostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath, subDirectory)).ToList();
using (var memoryStream = new MemoryStream())
{
using (var archive = new ZipArchive(memoryStream, ZipArchiveMode.Create, true))
{
files.ForEach(file =>
{
var theFile = archive.CreateEntry(file);
using (var streamWriter = new StreamWriter(theFile.Open()))
{
streamWriter.Write(File.ReadAllText(file));
}
});
}
return ("application/zip", memoryStream.ToArray(), zipName);
}
}
#endregion
#region Size Converter
public string SizeConverter(long bytes)
{
var fileSize = new decimal(bytes);
var kilobyte = new decimal(1024);
var megabyte = new decimal(1024 * 1024);
var gigabyte = new decimal(1024 * 1024 * 1024);
switch (fileSize)
{
case var _ when fileSize < kilobyte:
return $"Less then 1KB";
case var _ when fileSize < megabyte:
return $"{Math.Round(fileSize / kilobyte, 0, MidpointRounding.AwayFromZero):##,###.##}KB";
case var _ when fileSize < gigabyte:
return $"{Math.Round(fileSize / megabyte, 2, MidpointRounding.AwayFromZero):##,###.##}MB";
case var _ when fileSize >= gigabyte:
return $"{Math.Round(fileSize / gigabyte, 2, MidpointRounding.AwayFromZero):##,###.##}GB";
default:
return "n/a";
}
}
#endregion
}
}
SizeConverter function is used to get the actual size of our uploading files to the server.
IFileService.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace UploadandDownloadFiles.Services
{
public interface IFileService
{
void UploadFile(List<IFormFile> files, string subDirectory);
(string fileType, byte[] archiveData, string archiveName) DownloadFiles(string subDirectory);
string SizeConverter(long bytes);
}
}
Let’s add this service dependency in a startup.cs file
Startup.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.HttpsPolicy;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.OpenApi.Models;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using UploadandDownloadFiles.Services;
namespace UploadandDownloadFiles
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers();
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "UploadandDownloadFiles", Version = "v1" });
});
services.AddTransient<IFileService, FileService>();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(c => c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/v1/swagger.json", "UploadandDownloadFiles v1"));
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
}
}
}
Create a FileController & now inject this IFileService using Constructor injection inside this FileController.
FileController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using UploadandDownloadFiles.Services;
namespace UploadandDownloadFiles.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class FileController : ControllerBase
{
#region Property
private readonly IFileService _fileService;
#endregion
#region Constructor
public FileController(IFileService fileService)
{
_fileService = fileService;
}
#endregion
#region Upload
[HttpPost(nameof(Upload))]
public IActionResult Upload([Required] List<IFormFile> formFiles, [Required] string subDirectory)
{
try
{
_fileService.UploadFile(formFiles, subDirectory);
return Ok(new { formFiles.Count, Size = _fileService.SizeConverter(formFiles.Sum(f => f.Length)) });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
#endregion
#region Download File
[HttpGet(nameof(Download))]
public IActionResult Download([Required]string subDirectory)
{
try
{
var (fileType, archiveData, archiveName) = _fileService.DownloadFiles(subDirectory);
return File(archiveData, fileType, archiveName);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return BadRequest(ex.Message);
}
}
#endregion
}
}
We can test our APIs in both swagger and postman.
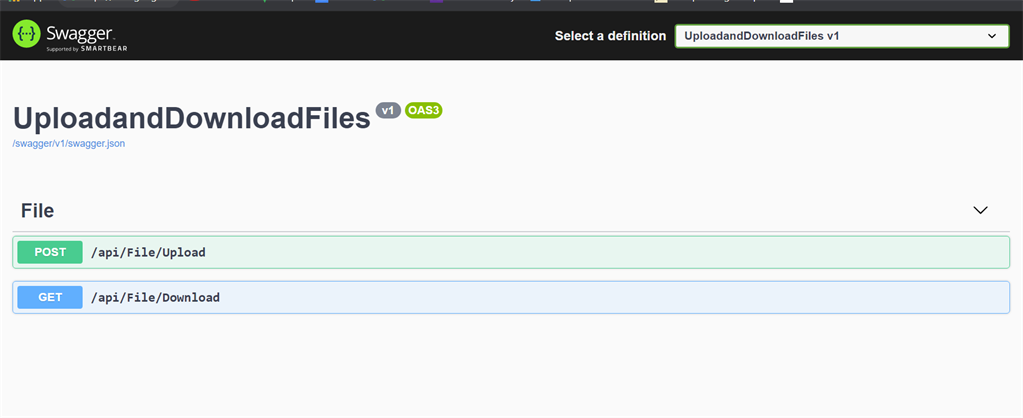
Here we see our two API’s which we have created to upload and download, so let’s test each of these individually.
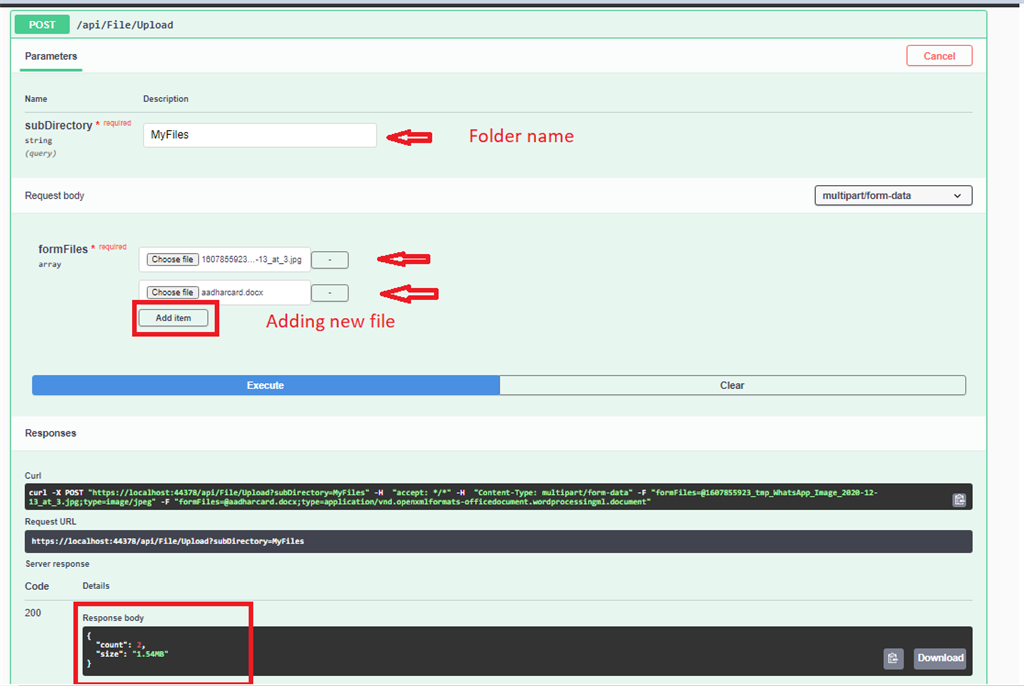
Pass the folder name inside the subDirectory and add files below to save inside the server and under the folder name. In response we see the total count of our files and the actual size of our entire files.
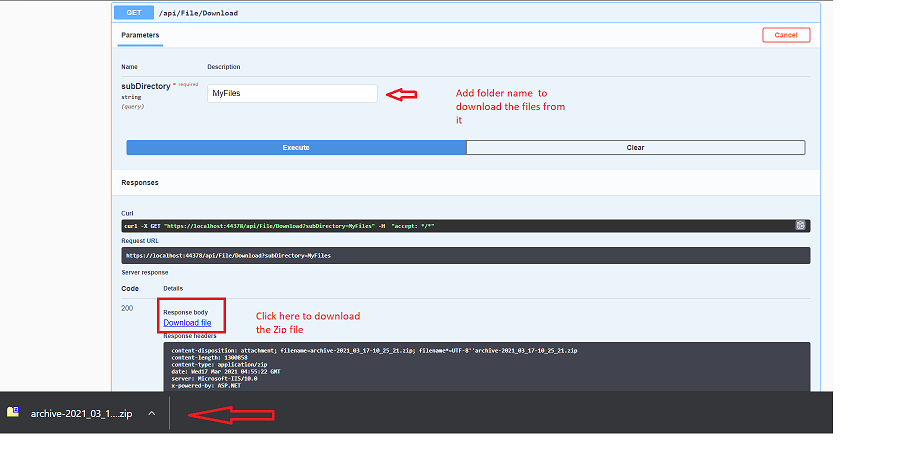
Now, will check with Download API. Since we have multiple files inside of our folder it will download as a Zip file where we need to extract that to check the files.
Source code
https://github.com/JayKrishnareddy/UploadandDownloadFiles
Conclusion
Hope this article gives you a clear understanding of Uploading and downloading multiple files to Web API using .Net 5.0.
Thanks for staying till the end and for reading as well. Please let me know your questions, thoughts, or feedback in the comments section. I appreciate your feedback and encouragement.