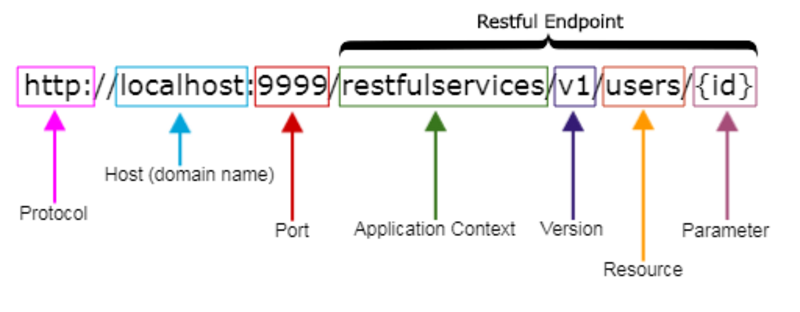
The main data representation in REST is referred to as a resource. A properly named resource makes an API simple to use and intuitive. That same API, when implemented incorrectly, may feel complicated and be challenging to use and comprehend. The following article will assist you in getting started when constructing the resource URIs for your new API.
Use Nouns to represent resources / Not Verbs
Always make sure that your URIs are named with nouns to specify the resource instead of using verbs. The URIs shouldn’t indicate any CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. Additionally avoid verb-noun combinations: hyphenated, snake_case, camelCase.
Bad examples:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/CreateItems/{item-id}❌
http://api.example.com/v1/store/getEmployees/{emp-id}❌
http://api.example.com/v1/store/update-prices/{price-id}❌
http://api.example.com/v1/store/deleteOrders/{order-id}❌
Good examples:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items/{item-id}✅
http://api.example.com/v1/store/employees/{emp-id}✅
http://api.example.com/v1/store/prices/{price-id}✅
http://api.example.com/v1/store/orders/{order-id}✅
Use Pluralized Nouns for resources
Use plural when possible unless they are singleton resources.
Bad examples (Typical and Singleton resources):
http://api.example.com/v1/store/item/{item-id}❌
http://api.example.com/v1/store/employee/{emp-id}/address❌
Good examples (Typical and Singleton resources):
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items/{item-id}✅
http://api.example.com/v1/store/employees/{emp-id}/address✅
Use hyphens (-) to improve the readability of URIs
Do not use underscores. Separating words with hyphens will be easy for you and others to interpret. It is more user-friendly when it comes to long-path segmented URIs.
Bad examples:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/vendormanagement/{vendor-id}❌
http://api.example.com/v1/store/itemmanagement/{item-id}/producttype❌
http://api.example.com/v1/store/inventory_management❌
Good examples:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/vendor-management/{vendor-id}✅
http://api.example.com/v1/store/item-management/{item-id}/product-type✅
http://api.example.com/v1/store/inventory-management✅
Use forward slashes (/) for hierarchy but not trailing forward slash (/)
Forward slashes are used to show the hierarchy between individual resources and collections.
Bad example:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items/❌
Good examples:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items✅
Avoid using file extensions
They are unnecessary and add length and complexity to URIs.
Bad examples:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items.json❌
http://api.example.com/v1/store/products.xml❌
Good examples:
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items✅
http://api.example.com/v1/store/products✅
Version your APIs
Always attempt to version your APIs. You can provide an upgrade path without making any fundamental changes to the existing APIs by versioning your APIs. You can also let users know that updated versions of the API are accessible at the following fully-qualified URIs.
http://api.example.com/v1/store/employees/{emp-id}
Introduction in any major breaking update can be avoided with the following /v2.
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items/{item-id}
http://api.example.com/v2/store/employees/{emp-id}/address
Use query component to filter URI collection
You will frequently come into requirements that call for you to sort, filter, or limit a group of resources depending on a particular resource attribute. Instead of creating additional APIs, enable sorting, filtering, and pagination in the resource collection API and give the input parameters as query parameters to meet this requirement.
http://api.example.com/v1/store/items?group=124
http://api.example.com/v1/store/employees?department=IT®ion=USA
Examples:
GET — Read employee with employee id 8345
example.com/employees/8345
POST — Create an employee
example.com/employees
PUT — Update employee with employee id 8345
example.com/employees/8345
DELETE — Delete employee with employee id 8345
example.com/employees/8345