Microsoft has recently introduced .NET Aspire, an opinionated stack for building resilient, observable, and configurable cloud-native applications with .NET 8+. Delivered through a collection of NuGet packages, .NET Aspire addresses specific cloud-native concerns, catering to the intricacies of modern, cloud-centric development.

More detailed information can be found here and here.
Given that cloud applications typically use a large number of services such as databases, messaging, and caching, it is sometimes not always easy to write integration tests. This article aims to explore the testing capabilities offered by .NET Aspire, extending beyond its role in advancing cloud application development.
While there may be limited documentation available for .NET Aspire at the moment, you can find an example with tests in the eShop Application.
Prepare sample app
A brief overview of the steps required to set up a .NET Aspire sample application. will be provided in this opening section. Microsoft offers comprehensive documentation that delves into the creation of a sample application, outlining its components and essential considerations. Furthermore, the source code discussed in this article is available on GitHub for reference.
Create the .NET Aspire starter application
To create a new .NET Aspire Starter Application, please use the following command:
dotnet new aspire-starter --output AspireSample
Run the app locally
The sample app is now ready for running:
dotnet run --project AspireSample/AspireSample.AppHost
Add test project
Now it’s time to add a test project and write a test for the WeatherForecast endpoint.
Create the .NET test project
Create the AspireSample.Tests project by running the following command:
dotnet new xunit -o AspireSample/AspireSample.Tests
Add the test project to the solution file by running the following command:
dotnet sln ./AspireSample/AspireSample.sln add ./AspireSample/AspireSample.Tests/AspireSample.Tests.csproj
Add the AspireSample class library as a dependency to the AspireSample.Tests project:
dotnet add ./AspireSample/AspireSample.Tests/AspireSample.Tests.csproj reference ./AspireSample/AspireSample.ApiService/AspireSample.ApiService.csproj
Set the IsAspireHost property of the AspireSample.Tests project file to true:
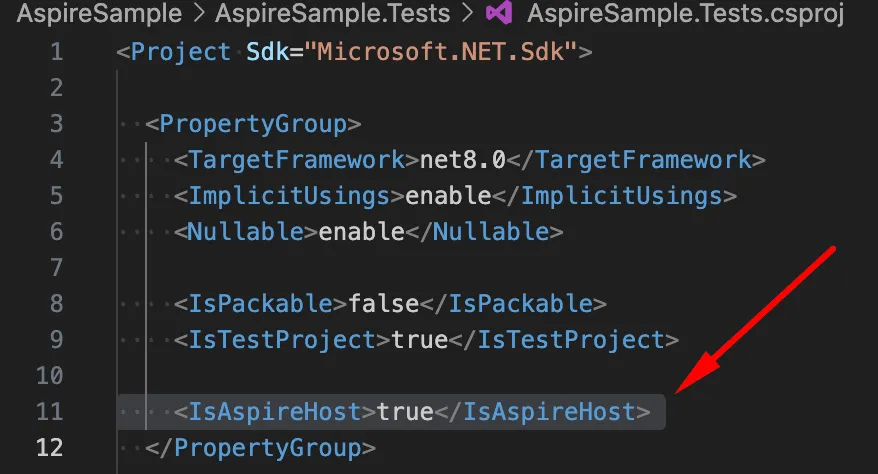
Create ApiServiceFixture
First, let’s add an ApiMarker to the ApiService project to enable referencing from a test project.
dotnet new interface -n IApiMarker -o AspireSample/AspireSample.ApiService - project AspireSample/AspireSample.ApiService/AspireSample.ApiService.csproj
To test the API endpoint, it’s necessary to include a test web host, which is provided by Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Testing package.
dotnet add ./AspireSample/AspireSample.Tests/AspireSample.Tests.csproj package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Testing
The Aspire.Hosting package (prerelease) is also essential for interacting with the core API and abstractions within the .NET Aspire application model.
dotnet add ./AspireSample/AspireSample.Tests/AspireSample.Tests.csproj package Aspire.Hosting - prerelease
Now let’s add Factory for bootstrapping an application in memory for tests.
public sealed class ApiServiceFixture : WebApplicationFactory<IApiMarker>, IAsyncLifetime
{
private readonly IHost _app;
public ApiServiceFixture()
{
var options = new DistributedApplicationOptions
{
AssemblyName = typeof(ApiServiceFixture).Assembly.FullName,
DisableDashboard = true
};
var appBuilder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(options);
_app = appBuilder.Build();
}
public async Task InitializeAsync()
{
await _app.StartAsync();
}
public new async Task DisposeAsync()
{
await base.DisposeAsync();
await _app.StopAsync();
if (_app is IAsyncDisposable asyncDisposable)
{
await asyncDisposable.DisposeAsync().ConfigureAwait(false);
}
else
{
_app.Dispose();
}
}
}
You can find further information about WebApplicationFactory here.
Add the first test
Finally, let’s add a test for the WeatherForecast endpoint.
public sealed class GetWeatherForecastEndpointTests(ApiServiceFixture fixture) : IClassFixture<ApiServiceFixture>
{
private readonly HttpClient _httpClient = fixture.CreateClient();
[Fact]
public async Task GetWeatherForecast_ShouldReturnsOk()
{
// Arrange
var requestUri = new Uri("weatherforecast", UriKind.Relative);
// Act
var response = await _httpClient.GetAsync(requestUri);
// Assert
Assert.Equal(HttpStatusCode.OK, response.StatusCode);
}
}
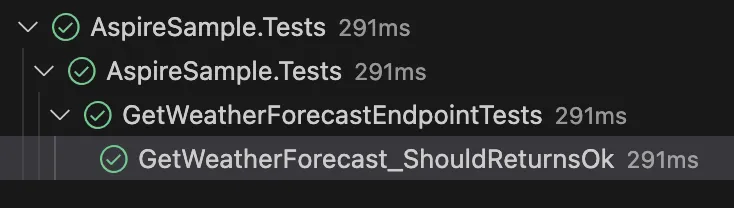
Run test
To run the test, please use the following command:
dotnet test ./AspireSample/AspireSample.Tests/AspireSample.Tests.csproj
Add external Weather API service
Now let’s assume that our ApiService takes weather data from a third-party service using HTTP requests.
The Weather API will be used in this article for educational purposes (but any other service can be used).
Let’s add a WeatherClient to interact with a third-party service.
internal sealed class WeatherClient(HttpClient httpClient) : IWeatherClient
{
public async Task<WeatherForecast[]> GetWeatherForecastAsync(
string city,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
ArgumentException.ThrowIfNullOrWhiteSpace(city);
string escapedCityString = Uri.EscapeDataString(city);
var requestUri = new Uri(
$"v4/weather/forecast?location={escapedCityString}×teps=1d&units=metric",
UriKind.Relative);
var response = await httpClient.GetFromJsonAsync<TomorrowWeatherForecast>(
requestUri,
cancellationToken);
return response is not null
? response.Timelines.Daily
.Select(x => new WeatherForecast(
DateOnly.FromDateTime(x.Time),
(int)x.Values.TemperatureAvg,
"Mild"))
.ToArray()
: [];
}
}
Configure and add our WeatherClient.
builder.Services.AddHttpClient<IWeatherClient, WeatherClient>(client =>
{
var baseAddress = builder.Configuration["WeatherClient:BaseAddress"];
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(baseAddress);
})
.AddHttpMessageHandler(() =>
{
var apiKey = builder.Configuration["WeatherClient:ApiKey"];
return new ApiKeyHandler(apiKey);
});
And use it in the WeatherForecast endpoint.
app.MapGet("/weatherforecast", async (
IWeatherClient weatherClient,
CancellationToken cancellationToken) =>
{
var forecast = await weatherClient.GetWeatherForecastAsync("new york", cancellationToken);
return forecast;
});
Let’s check that our application is still working.
dotnet run --project AspireSample/AspireSample.AppHost
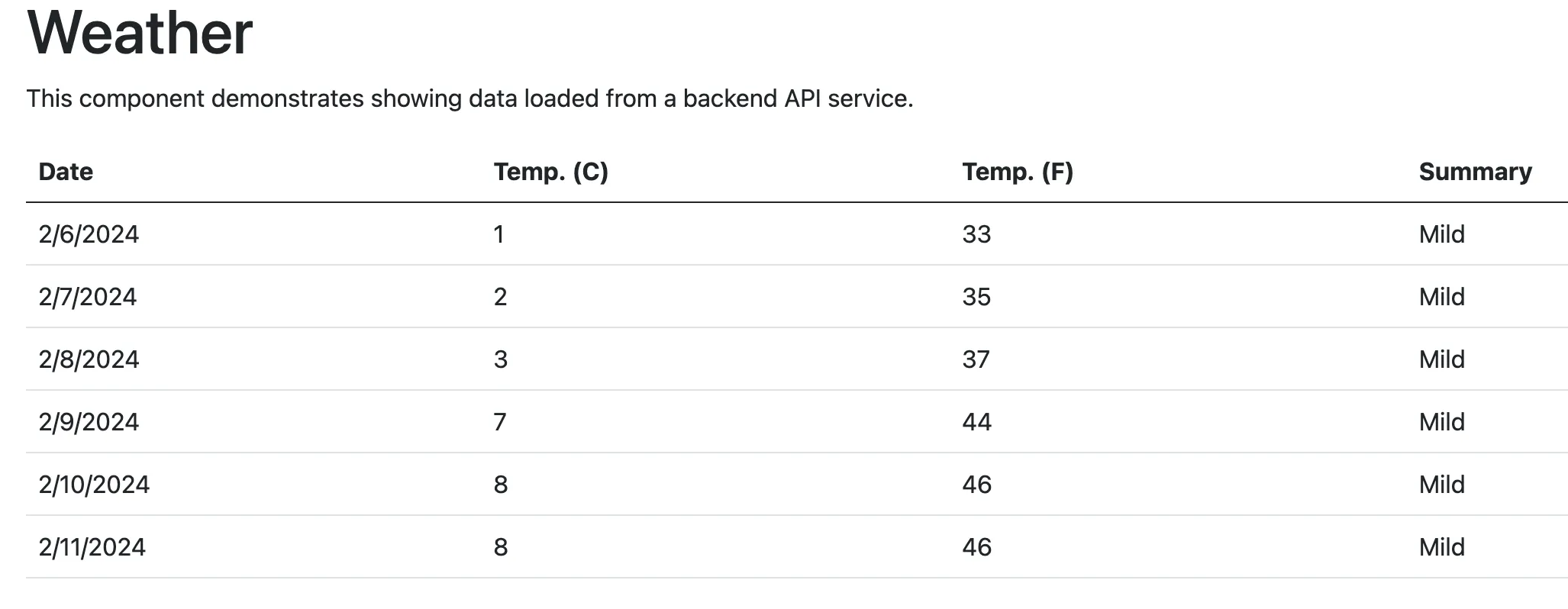
Our test runs successfully; however, it’s worth noting that relying on a third-party service for testing is not the best idea (especially for negative scenarios).
Mock external API
To address this situation, there are several approaches available:
- Mocking the HttpMessageHandler.
- Mocking the IWeatherClient interface.
- Completely replacing the third-party service.
Given our focus on integration tests, the most appropriate approach would be to entirely substitute the third-party service. Alternatively, WireMock.Net can serve as a viable solution. There are various ways to utilize WireMock.Net, but considering the focus of this article on the opportunities provided by .NET Aspire, the option of running WireMock.Net in a Docker container is explored.
Nick Chapsas has produced an informative video Writing robust integration tests in .NET with WireMock.Net, which provides valuable insights into utilizing WireMock.Net. I highly recommend watching it for a better understanding.
Setup WireMock.Net container
Sheyenrath/wiremock.net-alpine image will be used to launch the container.
var weatherApiService = appBuilder.AddContainer("weatherapiservice", "sheyenrath/wiremock.net-alpine", "latest")
.WithServiceBinding(
containerPort: 80,
name: "weatherapiservice",
scheme: "http");
_weatherApiEndpoint = weatherApiService.GetEndpoint("weatherapiservice");
Add WeatherApiServer
Also, the necessary settings must be made to configure the fake server.
public sealed class WeatherApiServer(string baseUrl)
{
private readonly IWireMockAdminApi _wireMockAdminApi =
RestClient.For<IWireMockAdminApi>(new Uri(baseUrl, UriKind.Absolute));
public Task SetupAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
var mappingBuilder = _wireMockAdminApi.GetMappingBuilder();
mappingBuilder.Given(builder => builder
.WithRequest(request => request
.UsingGet()
.WithPath("/v4/weather/forecast")
.WithParams(p => p
.Add(GetLocationParameter)
.Add(GetDaysTimeStepsParameter)
.Add(GetDaysUnitsParameter)
.Add(GetApiKeyParameter))
)
.WithResponse(response => response
.WithBody("""
{
"timelines": {
"daily": [
{
"time": "2024-01-30T11:00:00Z",
"values": {
"temperatureAvg": 2.01
}
},
{
"time": "2024-01-31T11:00:00Z",
"values": {
"temperatureAvg": 3.02
}
},
{
"time": "2024-02-01T11:00:00Z",
"values": {
"temperatureAvg": 4.03
}
}
]
}
}
""")
)
);
return mappingBuilder.BuildAndPostAsync(cancellationToken);
static ParamModel GetLocationParameter() =>
new()
{
Name = "location",
Matchers =
[
new() { Name = "ExactMatcher", Pattern = "new york" }
]
};
static ParamModel GetDaysTimeStepsParameter() =>
new()
{
Name = "timesteps",
Matchers =
[
new() { Name = "ExactMatcher", Pattern = "1d" }
]
};
static ParamModel GetDaysUnitsParameter() =>
new()
{
Name = "units",
Matchers =
[
new() { Name = "ExactMatcher", Pattern = "metric" }
]
};
static ParamModel GetApiKeyParameter() =>
new()
{
Name = "apikey",
Matchers =
[
new() { Name = "ExactMatcher", Pattern = "valid_api_key" }
]
};
}
}
Update ApiServiceFixture
Let’s configure the client to send requests to the fake server, and also launch the container.
protected override IHost CreateHost(IHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.ConfigureHostConfiguration(config =>
{
var settings = new Dictionary<string, string?>
{
{ "WeatherClient:BaseAddress", _weatherApiEndpoint.UriString },
{ "WeatherClient:ApiKey", "valid_api_key" }
};
config.AddInMemoryCollection(settings);
});
return base.CreateHost(builder);
}
public async Task InitializeAsync()
{
await _app.StartAsync();
var weatherApiServer = new WeatherApiServer(_weatherApiEndpoint.UriString);
await weatherApiServer.SetupAsync();
}
That’s all! All that remains is to run the test and make sure that everything works as expected.
Recap
This article explores the testing capabilities of .NET Aspire, Microsoft’s suite tailored for cloud applications. It guides readers through the process of setting up a sample application and integrating a test project to enhance functionality. Furthermore, it delves into simulating external services using WireMock.Net and .NET Aspire.
The source code discussed in this article is available on GitHub.
Thanks for reading!
• • •
Useful links
Introducing .NET Aspire: Simplifying Cloud-Native Development with .NET 8
.NET Aspire overview
Integration tests in ASP.NET Core
eShop — FunctionalTests
WireMock.Net
Nick Chapsas — Writing robust integration tests in .NET with WireMock.NET