Long polling is a server-push technique used in web applications to efficiently update clients with new information. Unlike traditional polling, long polling keeps the request open until the server has new data to send. This method is beneficial when you want to reduce the latency for data updates without overloading the server with frequent requests. In this blog, we’ll explore how to implement advanced long polling in .NET 6.
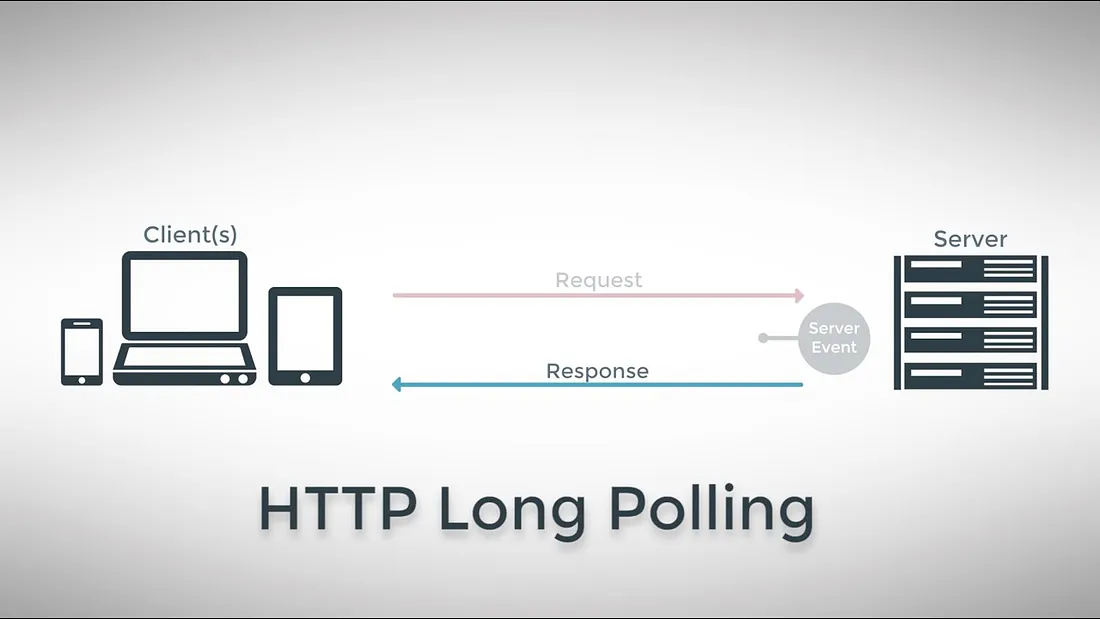
Understanding Long Polling
Long polling is an evolution of the HTTP polling technique. A client initiates a request to the server, which keeps the connection open until it can return fresh data. This strategy is particularly useful in scenarios where data updates are sporadic and unpredictable.
Setting up the project
First, ensure you have .NET 6 installed. Create a new ASP.NET Core Web API project, which will serve as the basis for our long polling implementation.
dotnet new webapi -n LongPollingDemo
cd LongPollingDemo
Implementing the server
We’ll create a service that simulates data updates and an API controller to handle long polling requests.
Data service
This service simulates a data source that updates at irregular intervals.
public class DataService
{
private readonly ConcurrentQueue<string> _messages = new ConcurrentQueue<string>();
public void AddMessage(string message)
{
_messages.Enqueue(message);
}
public bool TryGetMessage(out string message)
{
return _messages.TryDequeue(out message);
}
}
API Controller
The controller will handle client requests and use DataService to send responses.
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class LongPollingController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly DataService _dataService;
private readonly ILogger<LongPollingController> _logger;
public LongPollingController(DataService dataService, ILogger<LongPollingController> logger)
{
_dataService = dataService;
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpGet("poll")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Poll(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
try
{
while (!cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
if (_dataService.TryGetMessage(out string message))
{
return Ok(message);
}
await Task.Delay(1000, cancellationToken);
}
return new StatusCodeResult(StatusCodes.Status408RequestTimeout);
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Polling request cancelled.");
return new StatusCodeResult(StatusCodes.Status400BadRequest);
}
}
[HttpPost("send")]
public IActionResult Send([FromBody] string message)
{
_dataService.AddMessage(message);
return Ok();
}
}
Registering the service
In Program.cs, register DataService as a singleton.
builder.Services.AddSingleton<DataService>();
Client-Side implementation
Clients can use JavaScript to poll the server for updates.
async function pollServer()
{
while(true)
{
try
{
const response = await fetch('https://localhost:5001/longpolling/poll');
if (response.ok)
{
const message = await response.text();
console.log('New message:', message);
}
else
{
console.error('Polling error:', response.status);
break;
}
}
catch (error)
{
console.error('Polling failed:', error);
break;
}
}
}
pollServer();
Advanced concepts
Timeout management
Implementing a timeout for long polling requests is crucial. In the example above, CancellationToken is used to manage request timeouts.
Scalability concerns
Long polling can be resource-intensive, especially with a large number of clients. Consider load balancing and proper resource management.
Alternatives
For more efficient real-time communication, explore WebSockets or Server-Sent Events (SSE), which may offer better performance and scalability.
Conclusion
Long polling in .NET 6 is a powerful technique for server-to-client communication, especially when dealing with sporadic data updates. By following the example provided, you can implement a robust long polling solution in your ASP.NET Core applications. Remember to consider scalability and alternative technologies like WebSockets for more demanding scenarios.