In the article, we are going to examine how to optimize SQL queries and improve query performance by using SQL query optimization tips and techniques and many others.
Before going towards the main topic of SQL Query optimization, let us first understand the actual processing of query:
Query Processing
Query processing is defined as the process of extracting data from a database through a series of phases. This involves converting queries written in high-level languages, such as SQL, into a form that can be understood by physical implementations of databases, as well as optimizing SQL queries.
There are three major steps involved in query processing:
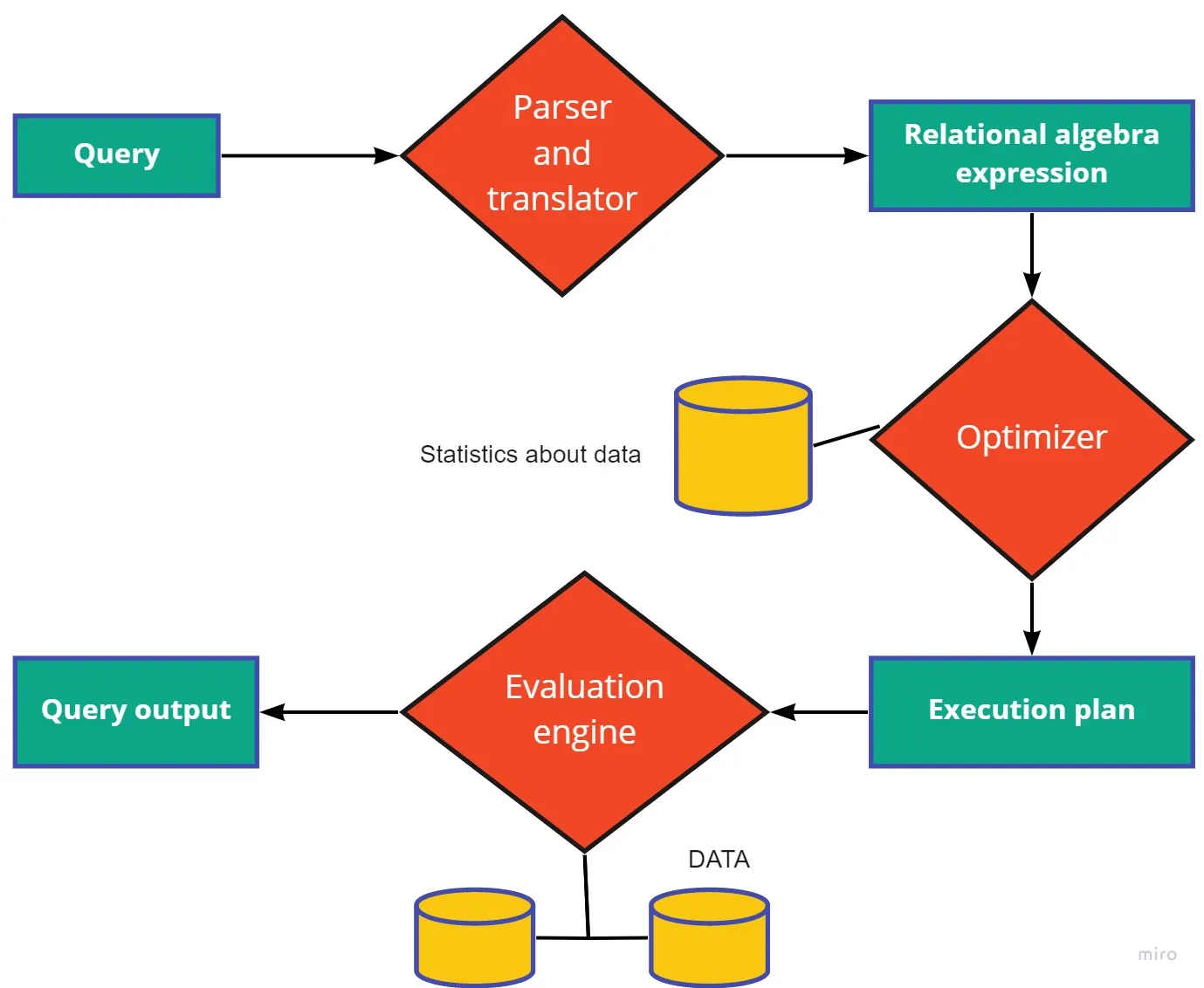
- Parsing and translation: Query processing begins with the parsing and translation of queries. Similar to a parser in a compiler, the parser checks the query syntax to see if the relations mentioned are in the database. SQL is suitable for human use because it is a high-level query language. Unfortunately, it cannot be used to represent system internals. Translation is therefore necessary. Relational algebra can be extended to represent the internal representation.
- Optimization: A SQL query can be written in many different ways. An optimized query also depends on how the data is stored in the file organization. A Query can also have different corresponding relational algebra expressions.
- Execution plan: an execution plan consists of a systematic step-by-step execution of primitive operations to fetch data from a database. There are different query costs associated with different evaluation plans for a particular query. The cost may include the number of disk accesses, CPU time for execution of the query, time of communication in the case of distributed databases.
• • •
SQL Query optimization
SQL Query optimization is defined as process of enhancing and speed the performance of a query in terms of execution time, the number of disk accesses, and many more cost measuring criteria. Access to the data should be in the fastest way possible to enhance the user experience while using the application.
Query optimization is a process of defining the most efficient and optimal way and techniques that can be used to improve query performance based on the rational use of system resources and performance metrics.
Purpose of SQL Query Optimization
The major purposes of SQL Query optimization are:
1. Reduce Response Time: The major goal is to enhance performance by reducing the response time. The time difference between users requesting data and getting responses should be minimized for a better user experience.
2. Reduced CPU execution time: The CPU execution time of a query must be reduced so that faster results can be obtained.
3. Improved Throughput: The number of resources to be accessed to fetch all necessary data should be minimized.
• • •
Top 10 SQL Query Optimization Techniques
1- SELECT fields, rather than using SELECT *
Use the SELECT statement optimally, instead of always fetching all data from the table. Fetch only the necessary data from the table.
Ineffective:
SELECT * FROM Business
Effective:
SELECT name, age, gender FROM Business
This query is much simpler, and only pulls the required details from the table.
• • •
Avoid DISTINCT in SELECT query
SELECT DISTINCT is a simple way of removing duplicates from a database. SELECT DISTINCT works to generate distinct outcomes by using the GROUP BY clause, which groups all the fields in the query. However, a large amount of processing power is required to do this. So, avoid DISTINCT in SELECT queries.
Ineffective:
SELECT DISTINCT FName, LName, Country FROM Customers
Effective:
SELECT name, age, gender FROM Business
Unduplicated records are returned without using SELECT DISTINCT by adding more fields.
• • •
Indexing
Indexing in SQL Server helps retrieve data more quickly from a table, thereby giving a tremendous boost to SQL query performance.
Use a covering index to reduce the time needed for the execution of commonly used statements.
CREATE INDEX index_optimizer ON Business(id);
• • •
To check the existence of records, use EXISTS() rather than COUNT()
Both EXISTS() and COUNT() methods can be used to check the existence of a record entry in the table.
The EXISTS() method is more effective as it exits processing as soon as it finds the first entry of the record in the table.
The COUNT() method would scan the entire table to return the number of records in the table that match the provided constraint.
SELECT count(id) FROM Business
EXISTS (SELECT (id) FROM Business)
• • •
Limit your working data set size
The less data retrieved, the faster the query will run. Instead of adding too many client-side filters, filter the data at the server as much as possible. This limits the data sent on the wire, and you will be able to see the results much more quickly.
• • •
Use WHERE instead of HAVING
The HAVING clause filters the rows after all the rows are selected. It works just like a filter.
HAVING statements are determined in the SQL operating order after WHERE statements. Therefore, it is quic4ker to execute the WHERE query.
Inefficient:
SELECT c.ID, c.CompanyName, b.CreatedDate FROM Business b
JOIN Company c ON b.CompanyID = c.ID
GROUP BY c.ID, c.CompanyName, b.CreatedDate
HAVING b.CreatedDate BETWEEN ‘2020-01-01’ AND ‘2020-12-31’
Efficient
SELECT c.ID, c.CompanyName, b.CreatedDate FROM Business b
JOIN Company c ON b.CompanyID = c.ID
WHERE b.CreatedDate BETWEEN ‘2020-01-01’ AND ‘2020-12-31’
GROUP BY c.ID, c.CompanyName, b.CreatedDate
• • •
Ignore linked subqueries
A linked subquery depends on the query from the parent or from an external source. It runs row by row, so the average cycle speed is greatly affected.
Inefficient:
SELECT b.Name, b.Phone, b.Address, b.Zip, (SELECT CompanyName FROM Company WHERE ID = b.CompanyID) AS CompanyName FROM Business b
For each row returned by the external query, the inner query is run every time. Alternatively, JOIN can be used to solve these problems for SQL database optimization.
Efficient
SELECT b.Name, b.Phone, b.Address, b.Zip, c. CompanyName FROM Business b
JOIN Company c ON b.CompanyID = c.ID
• • •
Summary
In this article, we’ve covered the some tips for optimizing SQL queries. The most important part is learning the rules of how to use and understanding the nuances of working with the main objects in a database, such as tables and indexes. With these skills, optimizing and analyzing SQL should be fun and simple.